ATLAS
ATLAS Approaching a Breakthrough in Diboson Polarization with Run-3 Data
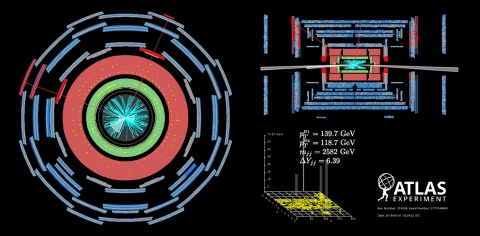
The study of the polarisation of vector boson scattering (VBS) processes provides a unique test of the Higgs mechanism’s role in taming high-energy electroweak interactions, making it indispensable for fundamental physics for the last decades. As…
Read moreTracing the Path to Precision: The Historical Evolution of Electroweak Physics at the LHC
The unification of the electromagnetic and weak-nuclear forces into an electroweak theory was one of the major breakthroughs of 20th century particle physics. In the 1960s, Steven Weinberg, Sheldon Glashow, and Abdus Salam proposed that these two…
Read moreATLAS hones in on Higgs-Boson Couplings to Heavy Flavour Quarks
Candidate event for the ZH → μμ cc process, where a Z boson and a Higgs boson decay to two muons (red tracks) and two charm-tagged jets (blue cones). (Image: ATLAS collaboration) In the summer of 2024, the ATLAS collaboration released two new…
Read moreExtended Scalar Sectors are considered from all angles at CERN
It has been more than ten years since the discovery of the first scalar particle at the electroweak scale. This particle was discovered at the LHC in 2012, and it was quickly found to be a scalar that is compatible with the Higgs boson predicted by…
Read moreLHC Run 3: A Marathon of Progress and Perseverance
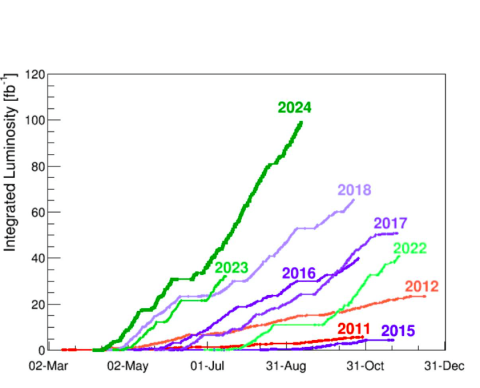
Earlier this month, the Large Hadron Collider reached an unprecedented milestone of 100 inverse femtobarns – equivalent to 10 million billion collisions – delivered to the ATLAS and CMS experiments in 2024, with 28 days of proton-proton collisions…
Read moreATLAS Operations: Progress and Highlights from 2023/2024
Great progress has been made in the ATLAS operation since the last EP news article. There we presented the fantastic Phase-I upgrades of the ATLAS detector installed during LS2, described the steps towards their commissioning, and summarized…
Read moreATLAS releases 2015 and 2016 proton–proton datasets for public research use
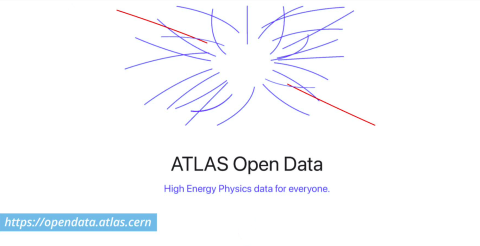
The ATLAS Collaboration has announced the release of 7 billion proton–proton collision events, alongside 2 billion simulated events, in the collaboration’s first release of open data for scientific research. The open data, available through CERN’s…
Read moreATLAS Open Data: Ushering in Transparency and Collaboration in Particle Physics Research
The ATLAS Collaboration at CERN,has been leading efforts to promote transparency and accessibility through its comprehensive open data initiatives. These efforts are designed to benefit researchers, educators, and the public, enhancing both…
Read moreGroundbreaking Observation of Quantum Entanglement in Top Quarks at the LHC
Researchers using the ATLAS detector at CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) have achieved a breakthrough: the first observation of quantum entanglement in top quark pairs. This discovery, analyzing proton-proton collisions at incredibly high energies…
Read moreA high-dimensional jet-powered measurement of the strong force
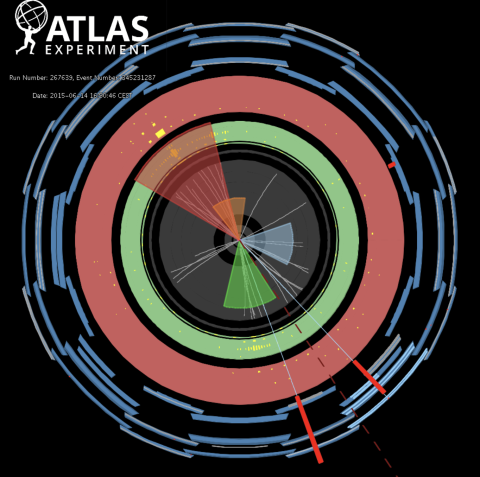
Top image: An event display of a high-momentum Z boson event in the ATLAS detector associated with a number of “jets”, which are complex clusters of particles created via interactions mediated by the strong force. Precise measurements of fundamental…
Read more